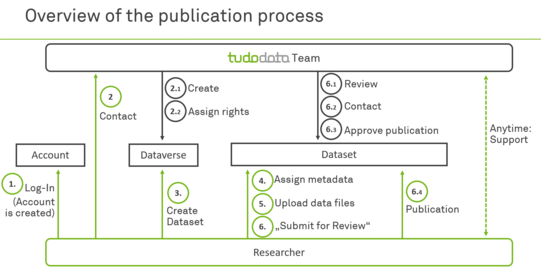
The data repository TUDOdata
TUDOdata is TU Dortmund University's data repository. Here, researchers can securely store, archive, and publish their research data. TUDOdata assigns each dataset a persistent identifier (a DOI), the datasets are enriched with additional information in the form of metadata, and published datasets are available Open Access.
Frequently asked questions
tudodata is available at https://data.tu-dortmund.de.

Contact the TUDOdata team:
- by e-mail: fdm@tu-dortmund.de
- in tudodata via "Support" or "Contact"
Information on the TUDOdata software can be found in the Dataverse User Guide.
You can find the terms of use here: TUDOdata Betriebsregelung (in German)
You can find the privacy policy here: Privacy Policy
You can find the imprint here: Imprint
Deposit license for publishing datasets in TUDOdata
This is the English version of data deposit license for tudodata. This version is for information purposes only. For explicit legal questions, only the German version applies.
1. Non-exclusive right of publication
By accepting this license, TU Dortmund University (hereinafter referred to as the “Operator”) is granted the non-exclusive right to store the deposited resource and its metadata, to multiply, globally publish and copy it as long as these measures are required for maintaining TUDOdata.
2. Format conversions
By accepting this license the operator is granted the right to on convert the resource to other electronic and physical formats where necessary (e.g. migration, accessibility, indexing)and to process them in accordance with paragraph 1.
3. Exemption from third party rights
The data provider assures that the work to be published or parts of it do not violate the rights of third parties. If alleged or actual violations of third-party rights are asserted after publication, the data provider assures to inform the operator immediately.
The data provider indemnifies the operator against all third-party claims, in particular claims for copyright and personal rights violations, which may be asserted against the operator in connection with the execution of the contractual rights, upon first request. The publishing party must inform the operator immediately of any infringements of the contractual rights of which they become aware.
The Operator is entitled to take appropriate measures to defend itself against third-party claims or to pursue its rights. The publishing party must coordinate their own measures with the operator in advance.
The indemnification also includes the reimbursement of costs incurred by the Operator as a result of legal prosecution/defense.
4. Forwarding for national collection mandates
By accepting this license, the operator is granted the right to pass on the resource and its metadata for the purposes of national collection mandates. The institution responsible for collecting the data is granted the same rights by the data provider as the operator.
5. Operating regulations
In addition to this license, the operating regulations for tudodata apply
At the top right of the header is a button with the two options "English" or "German".
Please note that some elements in TUDOdata are not translated into German. The recommended language for this software is English.
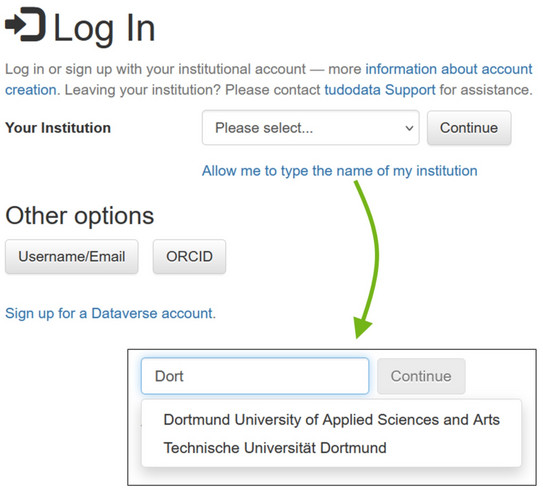
For TU and UARuhr members, logging in works via the institutional accounts, i.e. you do not need a separate account.
In the header at the top right, click on "Log In" and then on "Your Institution". You have two options here:
- Select your institution from the list or
- Click on "Allow me to type the name of my institution" and enter parts of the institution name
"Continue" and log in with your institutional account.
---
External users have the option of creating a separate TUDOdata account ("sign up for a Dataverse account") or logging in with the ORCiD.
At the beginning you do not yet have any access rights.
With TUDOdata, we have the task of providing a curated data repository in which data can be published in a findable, comprehensible, and reusable way. To this end, we have developed an organizational structure that reflects the structure of TU Dortmund University.
To get the correct access rights for you, please contact us directly in TUDOdata via "Support" or "Contact" or write us an email to fdm@tu-dortmund.de and give us the following information:
- Which department, which working group, which collaborative project (or similar) do you belong to?
- For which project would you like to upload data to TUDOdata?
- What is the name of the sub-dataverse in which the data is to be stored?
Once you have contacted us, the tudodata team can create a sub-dataverse and grant you access rights (important: you must log in to the system once beforehand).
If you have any questions or you would like to talk to us directly, we will be happy to arrange an individual consultation meeting.

Navigate to the your sub-dataverse and click on "+ Add Data" in the top right-hand corner and then on "New Dataset" (Tip: The easiest way to find accessible dataverses is under your account name in the top right-hand corner and then under "My Data").
In the following window, you must fill in all the metadata marked with a red asterisk. These are mandatory and are as follows:
- Title
- Author
- Point of Contact
- Description
- Subject
In fields 2-5, you can add additional entries on the right-hand side using the "+" (Add).
Finally, you can add data to the data record by dragging it into the browser ("Drag and Drop") or selecting the files and folders ("Select Files to Add").
You can then save the data record.
Important: After saving, you can still change all metadata and also delete files or add new files. The version of the data record is only unchangeable after publication.
Note: After the initial save, you can add and edit further metadata fields (including the license) by clicking on "Edit Dataset".
- Choose meaningful file and folder names
- Use open file formats instead of proprietary formats, for example:
- .txt, .odt, .docx for editable text, PDF-A for documents
- .jpeg, .tiff, .png for images
- .wav, .mpr for audio
- .mkv, .mp4 for video
- .csv, .ods, .xlsx for tabular data
- Tip: For many tabular formats, TUDOdata performs a conversion and the file is automatically converted into a csv file. Both the original file and the csv file are then available for download
- An overview of recommended file formats for long-term availability can be found on the lzv.nrw page (in German).
- Add a readme file and a license file to your dataset.
- If the dataset is downloaded by other researchers, the information will not be lost and the data can be reused
- The readme file should contain important metadata, such as
- title
- authors
- contact details
- DOI of the dataset in tudodata
- Reference to a related text publication
- Suggestion for citation of the dataset
- Description of the research project
- Description of the dataset to enable subsequent use
- License
- The license file lists the license with the detailed license text
- In tudodata you will find templates from the TUDOdata team for readme and license files, which you can adapt for your dataset: Template for readme file
- For a folder structure, use a zip archive for uploading
- Tip: Describe the used folder structure in the readme file
Note: Each dataset is curated and reviewed before publication. The criteria for evaluating the quality of a dataset can be found in the curation checklist.
To create a folder structure in TUDOdata, prepare your data in your local file system in the same way as the files and folders should be available for download in tudodata later.
Then create an archive (.zip file) of your data and upload this .zip archive. Tip: Under Windows, you can create a .zip archive by, for example, selecting the folders and files, right-clicking on them, and then selecting "Send to" and "ZIP-compressed folder".
TUDOdata automatically unpacks the archive and the prepared folder structure is retained.
In the dataset, under "Files" in the file view, there is the option to change the view ("Change View") with the two options "Table" (list of files) or "Tree" (hierarchical structure).
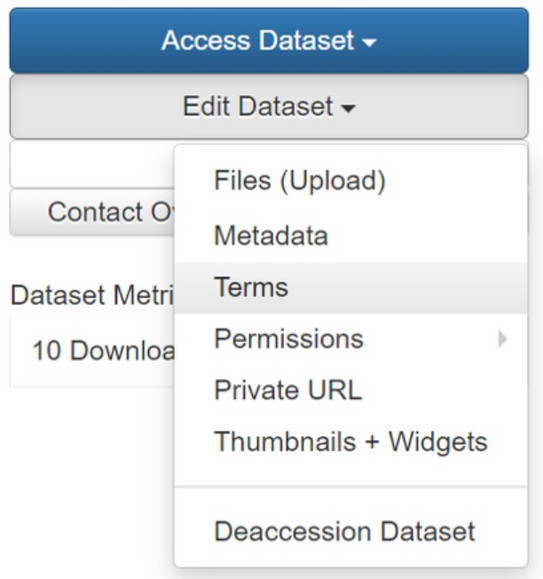
When you create a dataset in TUDOdata, the default setting is the CC-BY 4.0 license. This setting can only be changed in the second step, i.e. you cannot select a license other than the default license when you initially create the data record!
If, after creating and saving the dataset, you want to change the license, proceed as follows:
- Click on the corresponding data record
- Click on "Edit Dataset" at the top right and then on "Terms"
- In the box next to "License/Data Use Agreement" you can select the desired license
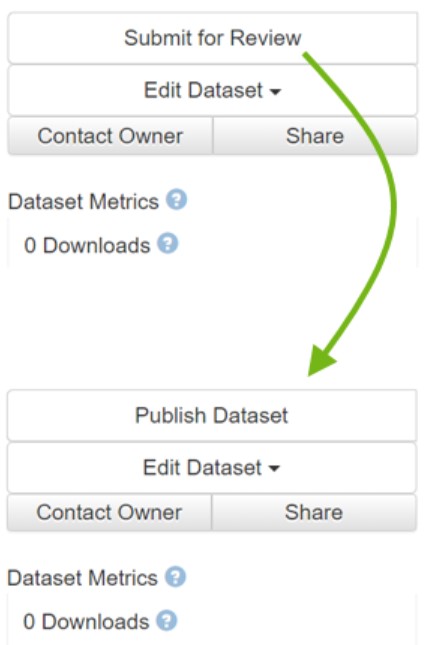
TUDOdata is a curated data repository, which means that the TUDOdata team will support you in the publication process and take a look at the dataset before publication to ensure that the principles of research data management are adhered to and that your dataset is FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable).
To submit a dataset for review, select your dataset and click on "Submit for Review" in the top right-hand corner.
The TUDOdata team will look at the dataset and contact you if there is room for improvement from an FDM point of view. This includes file naming, readme and license files, folder structures, metadata informations, and file types for ensuring reusability of the dataset. The criteria for evaluating the quality of a dataset can be found in the curation checklist.
If the dataset is accepted, you will receive the TUDOdata role "DatasetPublisher" for the dataset and you can publish the dataset yourself (the "Submit for Review" has then changed to "Publish" in the top right-hand corner).
A handout and more detailed instructions on "How do I publish my data in TUDOdata?" can be found in the Research Data Service publication.
Information on RDM can be found on the following pages or by contacting the Research Data Service at fdm@tu-dortmund.de
Further questions and instructions
No - you can also use TUDOdata for storing and archiving (10 years according to the rules of good scientific practice). If you create datasets and upload files, the data (sets) are not publicly accessible! The data is only available Open Access once it has been published.
Even if you do not publish the data, TUDOdata offers you a number of options: you can create private links to give other people reading access or you can give others write access to work together on a dataset.
Even without publication, you can save your data in TUDOdata in a way that it is findable and secure for you by assigning metadata.
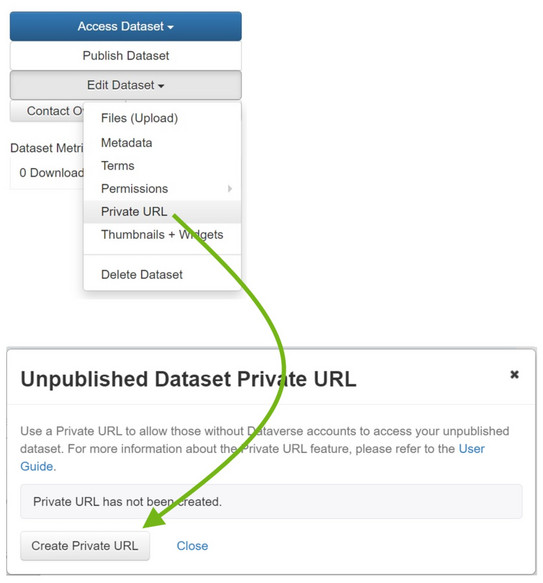
You have the option of creating a private link (private URL) for unpublished data records. Even if the dataset is not yet published, people who receive the link can have read access to the dataset. This is useful for submitted papers or articles, for example, to give reviewers the opportunity to examine the data without having to publish the dataset yet. Remember that all persons with the private link have full reading access to the dataset!
To do this, select your dataset and then click on "Edit Dataset" on the right-hand side. Select "Private URL". In the new window, you can now create a private link via "Create private URL". A success message will appear and you can copy the URL to the clipboard with "Copy to Clipboard" for further processing.
Aftewards, you can find the private URL in the upper area of the dataset view or via "Edit Dataset" and "Private URL". Here you can also deactivate the private URL again via "Disable Private URL".
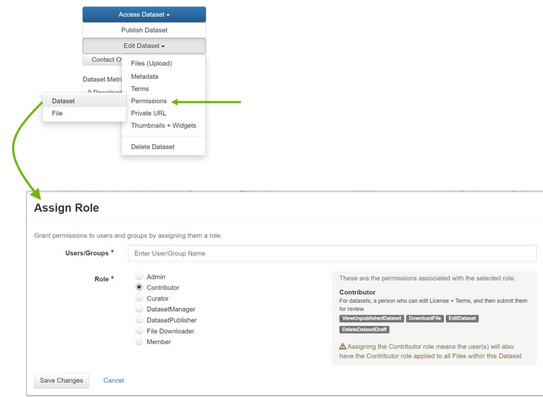
You have the option of giving other people write access to your dataset - the dataset can still be unpublished.
To do this, select your dataset and go to the corresponding settings: "Edit Dataset" -> "Permissions" -> "Dataset".
The users with access rights are displayed in the following window. You can now use "Assign Roles to Users/Groups" to assign access rights to individual persons or installed groups:
- In the "Users/Groups" field, type in part of the user/group name. TUDOdata filters the users/groups according to your input. You can then select the person/group.
- The "Role" field allows you to select the newly assigned role. When you select an element, the properties and access rights are displayed. As a rule, the "Contributor" role is a good choice to allow write access.
- Note: You have the option of assigning access rights that correspond to your own, but no higher access rights
This depends on whether the dataset is published or not.
- Unpublished datasets can be deleted again without any problems. To do this, click on the dataset, then on "Edit Dataset" and then on "Delete Dataset". The dataset, including all files, is then irrevocably deleted.
- This is not possible for published datasets!
- Please note that a published dataset has been assigned a persistent identifier (DOI) and must be persistently available. Deletion is therefore not intended, as otherwise the persistent identifier would point to an empty dataset.
- It is possible to "deaccession" a dataset and thus hide the files from external parties. However, the metadata is still visible if the dataset is accessed via the public DOI.
- To do this, navigate to the dataset and select "Edit Dataset" and then "Deaccession Dataset".
- You must then enter a reason and, if applicable, select the version to be blocked. Optionally, you can add an alternative link to the dataset.
- Notes:
- The dataset can then no longer be found by external users via the data repository. The metadata page can only be accessed via the DOI
- If the blocked dataset is accessed via the DOI, a special page with a note and the reason appears
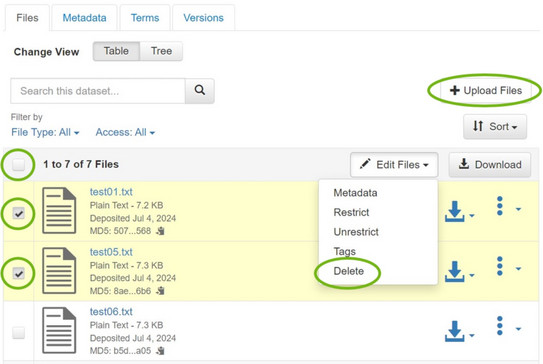
You can easily delete files from or add files to unpublished datasets. To add files, you can click on "Upload Files" after selecting the dataset. To delete files, select the desired files using the selection fields to the left of the file names, select "Edit Files" and then "Delete". You can also use the selection field to select all files in a dataset. You also have the possibility of replacing files: to do this, select the "Replace" option for the file in the right-hand area via "File Options" (symbol with 3 dots) and upload the new version of a file.
Please note that there is no versioning for unpublished data records, i.e. deleting and replacing files ist irrevocable.
---
With published datasets, a change to the files automatically leads to the creation of a new version of the dataset. In this case, a file remains in the previous dataset version when it is deleted and is deleted in the new, current version of the dataset. Users can still access the file via the old version. When adding a file, the system behaves in the same way: the file is added to the newly created dataset version.
Please note that versioning is only available for published datasets. There is no versioning option for a dataset that has not yet been published and all changes to the dataset are irrevocable!
Versioning runs automatically in TUDOdata. As soon as you change the metadata or the files of a published dataset, a new version is created. If you change files (add, delete, replace), TUDOdata automatically generates a new main version number (1.x, 2.x, 3.x, etc.). When changing the metadata, you can choose whether the major version number should be incremented or whether it is a minor release. In the latter case, the minor version number is incremented after the dot (1.1, 1.2, 1.3, etc.).
You can find the different versions in the "Versions" tab in the view of the dataset.
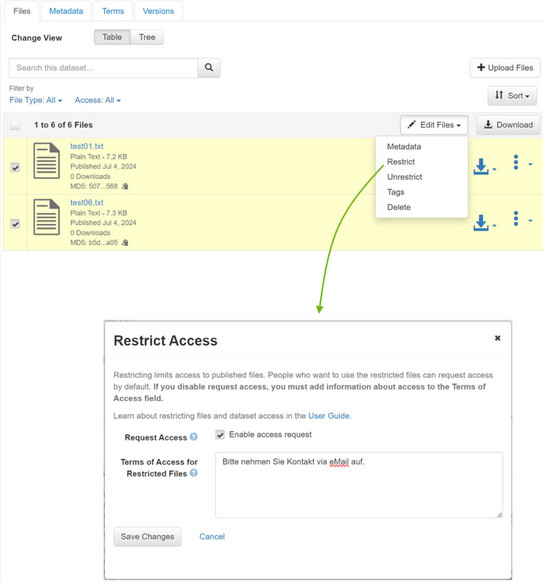
To do this, you have the option of restricting access to individual files. The files are then visible with file name, file type and size, but the content is not open accessible. A request for access can be sent to the contact persons.
To restrict access to individual files in a dataset, select them and go to "Restrict" via "Edit Files". In the window that appears, you have the option of activating the access request ("Enable Access Request") and you can enter the information text that should appear next to the blocked files (the procedure for users or requirements for the request are usually described here).
Locked files cannot be accessed Open Access until the lock is removed ("Unrestrict").
Go to your dataset, then click on "Edit Dataset" and "Metadata".
Notes:
- When you initially create a dataset, only a subset of the available metadata is displayed
- You can use the "+" symbol on the right-hand side to create additional entries, e.g. for authors or keywords
- In order to make the dataset as easy to find and reusable as possible, you should try to enter as much information as possible in the metadata (the readme file is also useful for this)
In the dataset view, you can click on "Link Dataset", then enter and select the target dataverse. Please note that you need the appropriate access rights for this.
Glossary
Below you will find the most important terms in connection with TUDOdata:
-
CC license
-
A Creative Commons license. The most commonly issued licenses for the publication of research data. The default license is CC-BY 4.0
-
-
Collection
-
Another term for a sub-dataverse
-
-
Dataverse
-
Has two meanings: Name of the software TUDOdata is based on, see https://dataverse.org/
-
Identifier for collections of datasets used for the internal organization and structuring of TUDOdata. For example, "TU Dortmund" and "resolvdata" are sub-dataverses of TUDOdata. A dataverse can be thought of as a folder for datasets and other dataverses
-
-
Dataset
-
A dataset consists of a set of research data. Each dataset is assigned a persistent identifier (DOI), receives metadata and a license.
FAIR FAIR principles, a central concept in research data management. Abbreviation for Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Re-Usable.
-
-
Metadata
-
Additional information about a dataset such as title, authors, contact details, description, discipline
-